An introduction to information security :-
An introduction to information security :-
“The practices of ensuring information is only read , heard, changed, modified, broadcast and otherwise used by those people who having write to do ” is called — Information Security.
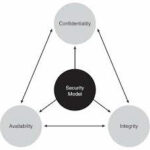
Three primary goals of Information Security is :-
- Confidentiality ( Keep data private )
- Integrity ( Ensure that data has not been modified in transit )
- Availability ( Data accessibility )
Confidentiality :-
There are two types of data:- data in motion as it moves across the network; and data at rest, when data is sitting on storage media (server, local workstation, in the cloud, and so forth). Confidentiality means that only the authorized individuals/systems can view sensitive or classified information. This also implies that unauthorized individuals should not have any type of access to the data. Regarding data in motion, the primary way to protect that data is to encrypt it before sending it over the network. Another option you can use with encryption is to use separate networks for the transmission of confidential data. Several chapters in this book focus on these two concepts.
Integrity:-
Integrity for data means that changes made to data are done only by authorized individuals/systems. Corruption of data is a failure to maintain data integrity.
Availability:-
This applies to systems and to data. If the network or its data is not available to authorized users—perhaps because of a denial-of-service (DoS) attack or maybe because of a general network failure—the impact may be significant to companies and users who rely on that network as a business tool. The failure of a network generally equates to loss of revenue.
My main intention to write this article to define my visitors about basic introduction about information security and basic terms used in information security. In my future articles i am going to write about more on information security that’s why it,s important for my visitors to know about basic information security terms. 🙂
Vulnerability :-
A Weakness which allows an attacker to break into / compromise a system’s security.Vulnerabilities can be found in protocols, operating systems, applications, and system designs.
Also Check :-
How to use Vega Web Vulnerability Scanner in Kali Linux
Free Online Vulnerability Scan with Qualys FreeScan
Find-out Vulnerable Website with Vulnerable Site Finder Tool
Exploit :- Code which allows an attacker to take advantage of a vulnerable system.
Also check :- How to use Searchsploit On Kali Linux
Payload :- Actual code which runs on the system after exploitation
Countermeasure :-
A countermeasure or mitigation is a device or process ( a safeguard) that is implemented to counteract a potential threat, which thus reduces risk.
Threat :-
A threat is anything that attempts to gain unauthorized access to, compromise, destroy, or damage an asset. Threats are often realized via an attack or exploit that takes advantage of an existing vulnerability.
Defense in Depth :-
This concept suggests that you have security implemented on nearly every point of your network. An example is filtering at a perimeter router, filtering again at a firewall, using IPSs to analyze traffic before it reaches your servers, and using host-based security precautions at the servers, as well. This is defense in depth. Using authentication and authorization mechanisms could also be part of a defense-in-depth approach.
The concept behind defense in depth is that if a single system fails, it does not mean that security has completely been removed from the equation.
Botnet :- A botnet is a collection of infected computers that are ready to take instructions from the attacker.
Check Also :- Find Out if Your Computer is Infected with a Bot
DoS and DDOS :-
Denial-of-service attack and distributed denial-of-service attack. An example is using a botnet to attack a target system. If an attack is launched from a single device with the intent to cause damage to an asset, the attack could be considered a DoS attempt, as opposed to a DDoS. Both types of attacks want the same result, and it just depends on how many source machines are used in the attack as to whether it is called a DoS or DDoS.
Also Check :-
How to Perform a DOS attack on Windows 7
What is Smurf DOS Attack and How to do it with BackTrack 5R3
How to Perform a DOS attack on a Website (LOIC Tool)
Perform DDOS Attack with Hping Command
Man-in-the-Middle attack :-
A man-in-the-middle attack results when attackers place themselves in line between two devices that are communicating, with the intent to perform reconnaissance or to manipulate the data as it moves between them. The main purpose is eavesdropping, so the attacker can see all the traffic.
Also Check :- How To do Man in Middle Attack using Ettercap in Kali Linux
This one is really big topic to write.
Hope you like my post.An introduction to information security. Please Share with others.
Also Check :-
An Introduction to IPSec Protocol
How to Use Wireshark to Capture, Filter and Inspect Packets
Nmap – Free Security Scanner For Network Exploration and Hacking