An Introduction to Network Firewalls Technologies :-
An Introduction to Network Firewalls Technologies :-
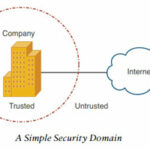
A ” Firewall ” is a hardware or Software device that enforces an access control policy between two or more security domains.
In my previous article i wrote about An introduction to information security . My main intention to write this article to introduce Firewall technologies to my blog visitors. 🙂
It is important to understand why we need the Firewall for the secure network. The reason why, in two words, is the Internet. Without doubt, the Internet has become an essential component of global commerce. The Internet provides global connectivity to millions of businesses and their customers, and for extremely low cost compared to traditional communication networks.
For example, corporate data might be confidential or critical to the operations of a business or to offering patient care, in which case it must be kept from prying eyes and protected from tampering. Similarly, the computers in a network might to be protected from outside interference’s so that they are kept stable and in good working order. 🙂
To protect these resources, the network must somehow be divided into trusted and un-trusted parts. The trusted portions of the network are known as Security domains; everything inside the security domains is protected from everything outside the domain.
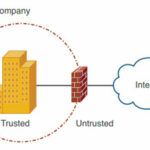
The most common and effective way to implement a security domain is to place a firewall at the boundary between the trusted and Un-trusted parts of the domain.
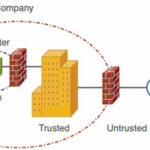
Sometime to make Data-center more secure company’s are implementing Multi-Security domain.
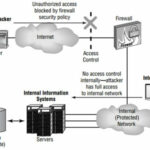
If the web servers are located somewhere inside the Security domain of their domain, then untrusted users would be granted access into the trusted environment. That isn’t necessarily bad, except that malicious users might be able to attack or compromise one the web-servers. Because the web-server is already a trusted resources, the malicious user might then use that server to attack other trusted resources. 🙁
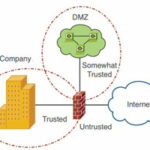
A better solution is to put the web servers into a security domain of their own, somewhere between the trusted internal network and the untrusted Internet. This is commonly called a demilitarized zone (DMZ).
With the addition of a third interface, the firewall can act as the boundary between a trusted domain, an untrusted public network, and a new “somewhat trusted” domain full of web servers.
For many organizations, a firewall is the single (and only) security device considered sufficient to protect the security of the network from external networks such as the Internet.
In above Figure , all traffic that must pass from the external network to the internal network (and vice versa) must pass through the firewall. The mandatory flow of traffic through the firewall enables security policy to be defined on the firewall, which determines the internal systems and applications that can be accessed from external parties.
A firewall can take one of the following approaches to its access control:-
- Permissive access control:- All traffic is allowed to pass through unless it is explicitly blocked.
- Restrictive access control:- No traffic is allowed to pass through unless it is explicitly allowed.
Firewall Technologies :-
Packet Filters :-
A packet filtering firewall represents the first generation of firewalls. The most basic packet filter firewall inspects traffic based on Layer 3 parameters (such as source or destination IP address). Packet filtering rules determine the types of traffic that are permitted access or denied access based on these parameters.
Traffic types can be defined by the following:-
- Layer 3 parameters such as source/destination IP address and IP protocol type (e.g., TCP, UDP, or ICMP)
- Layer 4 (e.g., TCP, UDP, or ICMP) parameters such as TCP/UDP source or destination port. TCP/UDP ports identify the upper-layer application protocol data contained within the packet (e.g., HTTP, DNS, or FTP).
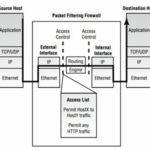 All traffic arriving into the external interface of the firewall is analyzed against an access list (a list of rules) that define which traffic flows should be permitted or denied. The firewall processes each rule until a match is made against the packet being inspected, and the appropriate action (permit or deny) is then applied.
All traffic arriving into the external interface of the firewall is analyzed against an access list (a list of rules) that define which traffic flows should be permitted or denied. The firewall processes each rule until a match is made against the packet being inspected, and the appropriate action (permit or deny) is then applied.
A packet filtering firewall only operates up to Layer 3 (some can inspect Layer 4 parameters as well) of the OSI model. It does not understand the higher layer levels such as the application layer (Layer 7).
Note :- A packet filtering firewall is essentially a router with access control rules configured.
Application Layer Gateways :-
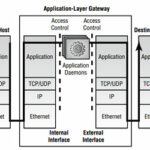
An application-layer gateway firewall is commonly referred to as a proxy based firewall, because it proxies application-layer connections on behalf of other clients. The application-layer gateway is vastly different from a packet filtering firewall in approach—all access is controlled at the application layer (Layer 7 of the OSI model), and no client system ever communicates directly with a server system.
An application-layer gateway provides daemons or services (server-side components) that emulate the services on the destination server that a client wishes to connect to. This allows clients to connect to the application-layer gateway rather than the destination server.
For each application that needs to be supported through the gateway, an appropriate application daemon must be available for and installed on the gateway. Most application-layer gateways also provide access control, regulating which hosts can use which services.
Note :- The application-layer gateway introduces a greater level of security than a packet filtering firewall, because all connections to the outside world are made by the application-layer gateway and the application-layer gateway ensures all received traffic from either client or server at the application layer is legitimate.
Stateful Packet Inspection :-
Stateful packet filtering (SPF) requires that a firewall keep track of individual connections or sessions as packets are encountered. The firewall must maintain a state table for each active connection that is permitted, to verify that the pair of hosts is following an expected behavior as they communicate. As well, the firewall must inspect traffic at Layer 4 so that any new sessions that are negotiated as part of an existing connection can be validated and tracked. Tracking the negotiated sessions requires some limited inspection of the application layer protocol.
Characteristics of a Stateful Packet Filter :-
Check my article :- What is Stateful Packet Inspection Firewall
Top network Firewalls Providers :-
Hope you like my post.An Introduction to Network Firewalls Technologies. Please Share with others.
Also Check :-
Most Common Interview Questions on OSI model
The OSI Model’s Seven Layers Defined and Functions Explained